In the user interface and Help, the term "asset" is synonymous with the term "object" and is used to reflect the business perspective of a company's IT assets.
At the center of Alfabet are applications which are products that provide the business with functionality. The application has relationships to other assets in IT.
application
An application is a complete installation of a software offering a functionality to an end user. The application might consist of or require other technical components to run.
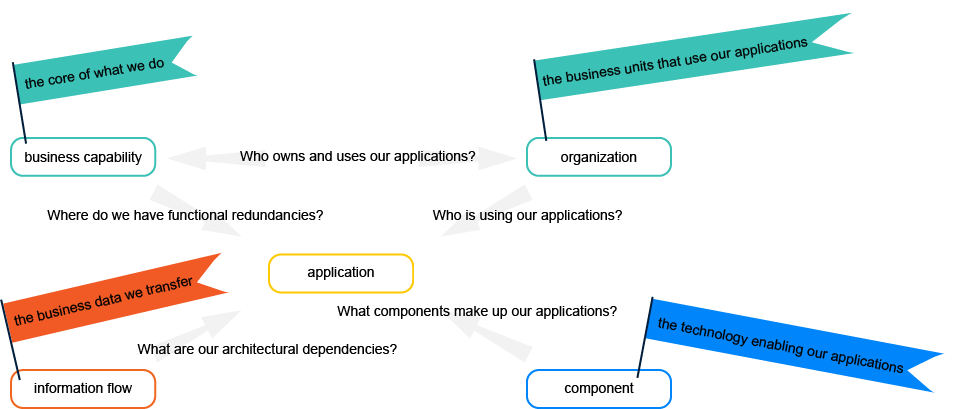
An application supports the business to fulfill its high-level business objectives, referred to as business capabilities . Whether your company captures how applications support business capabilities or business processes will depend on your company's methodology. Organizations use applications to fulfill the business's objectives. Further, the application transfers business data to other applications via information flows . Many technological components such as operation systems, databases, and web servers are used to build the application.
business capability
A business capability is a high-level description of what is done in a company to meet its business objectives. Market development, product development, and support and services are examples of business capabilities.
business process
A business process is an activity or set of activities that represent work required to accomplish a specific organizational objective. Marketing services, selling products, delivering services, distributing products, invoicing for services, and accounting for money received are examples of business processes.
organization
An organization is a business-driven governance structure such as an administrative or functional unit in the company.
business data
Business data is the information exchanged between applications or components. Business data is transferred by information flows.
information flow
An information flow describes the exchange of business data between source and target applications.
component
A standard component is a reusable block of functionality that provides technical functionality to an application or to the platforms that an application runs on. Components do not usually provide functionality to end users. Typical components are operating systems, database management systems, or application servers. A component that is used in an application's platform is a local component and is not is reusable.
The data captured in Alfabet is based on a class model. Every object is an instance of an object class . Each object will have attributes and references that describe its characteristics in the IT landscape. An overview of classes describes the basic attributes and references that can be captured for each object class.
object
Alfabet is based on a class model. An object refers to an instance of an object class for which data can be captured such as an application, component, etc. The term "object" is synonymous with the term "asset".
object class
Alfabet is based on a class model that includes classes like Application, Business Capability, Component. etc. Each object is an instantiation of its object class. For example, an application like SAP@CRM System is an instantiation of the class Application.
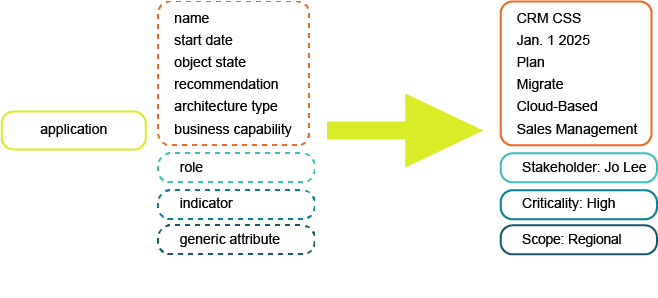
In the example above, an application is an instance of the class Application. An object will have many standard attributes that describe the object. For example, an application has a set of standard attributes that include Name, Version, Start Date, and End Date. Applications have many more standard attributes that allow the application to be described in rich detail. Some of the attributes will be references to objects in other classes. An application may also have roles , indicator types , and extended attributes defined. For example, the class Application has a reference to the class Application Group, which indicates that the application belongs to the application group.
role
A role describes the functional relationship that a user or organization has for an object.
indicator type
An indicator type is a dimension of measurement regarding the performance of an object in the IT landscape. Example indicator types are Business Relevant or Number of Users. The indicator is the value defined for an indicator type in the context of an object in the IT landscape.
extended attribute
A extended attribute is a custom attribute that allows the ad-hoc capture of information for a class.

